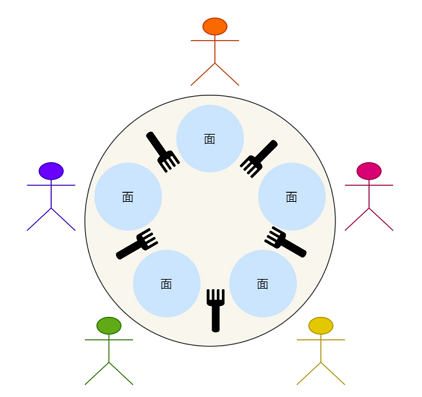
哲学家问题
问题阐述
- 有5个哲学家共用一张圆桌,分别坐在周围的5张椅子上
- 在圆桌上有5个碗和5只筷子,他们的生活方式是交替地进行思考和进餐。
- 平时,每个哲学家进行思考,饥饿时便试图拿起其左右最靠近他的筷子,只有在他拿到两只筷子时才能进餐。
- 进餐完毕,放下筷子继续思考。
代码及问题
版本1
public class SmartPersonProblem {
static final int total = 5;
static class philosophy extends Thread{
int number;
ArrayList<Semaphore> fork;
public philosophy(int i, ArrayList<Semaphore> fork){
this.number = i;
this.fork = fork;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "正在思考");
Semaphore left = fork.get(number);
Semaphore right = fork.get((number + 1) % total);
try {
left.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好左left叉子");
right.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好右right叉子");
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------eating");
left.release();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------放下左left叉子");
right.release();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------放下右right叉子");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Semaphore> semaphores = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);
semaphores.add(semaphore);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new philosophy(i,semaphores)).start();
}
}
}
|
问题
出现死锁

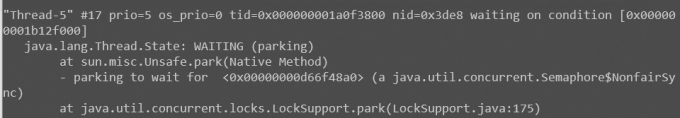
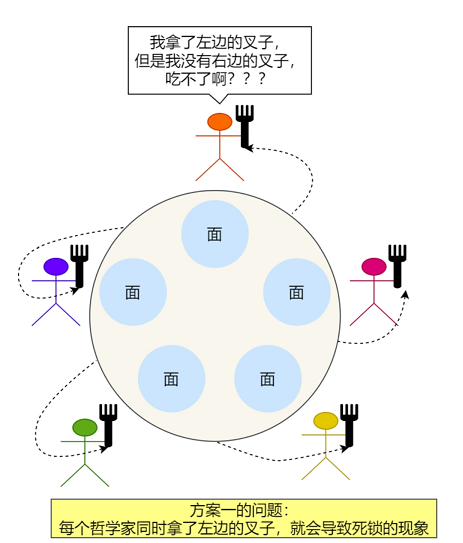
原因
当哲学家同时拿起左叉子,每个线程均会处在等待状态下,因为每位哲学家的右叉子都为空,下图所示
版本2
解决方案
版本一存在同时竞争左边叉子导致死锁的现象,那么不妨在拿叉子前,加一个互斥信号量(Semaphore),来对临界资源进行限制
public class SmartPersonProblem {
static final int total = 5;
static class philosophy extends Thread{
int number;
ArrayList<Semaphore> fork;
Semaphore togetherSemaphore;
public philosophy(int i, ArrayList<Semaphore> fork,Semaphore togetherSemaphore){
this.number = i;
this.fork = fork;
this.togetherSemaphore = togetherSemaphore;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "正在思考");
Semaphore left = fork.get(number);
Semaphore right = fork.get((number + 1) % total);
try {
togetherSemaphore.acquire();
left.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好左left叉子");
right.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好右right叉子");
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------eating");
left.release();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------放下左left叉子");
right.release();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------放下右right叉子");
togetherSemaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Semaphore> semaphores = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);
semaphores.add(semaphore);
}
Semaphore togetherSemaphore = new Semaphore(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new philosophy(i,semaphores,togetherSemaphore)).start();
}
}
}
|
缺陷
在上述代码,可以解决哲学家就餐问题(不会产生死锁状况),但是有个缺陷,如下
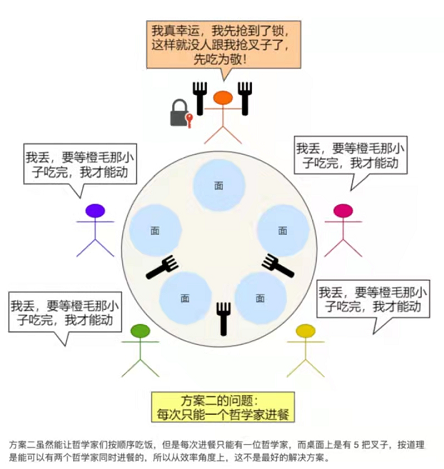
虽然可以让哲学家都吃到饭,但一次只能有一位哲学家进行吃饭,按理来说,最优化方案应该是一轮有两个哲学家进行吃饭
版本3
优化方案
- 偶数编号的哲学家———先拿左边的叉子,后拿右边的叉子
- 奇数编号的哲学家———先拿右边的叉子,后拿左边的叉子
(在版本1进行优化)
代码
public class SmartPersonProblem {
static final int total = 5;
static class philosophy extends Thread{
int number;
ArrayList<Semaphore> fork;
public philosophy(int i, ArrayList<Semaphore> fork){
this.number = i;
this.fork = fork;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "正在思考");
Semaphore left = fork.get(number);
Semaphore right = fork.get((number + 1) % total);
try {
if(number % 2 == 0){
left.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好左left叉子");
right.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好右right叉子");
}else{
right.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好右right叉子");
left.acquire();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------拿好左left叉子");
}
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------eating");
left.release();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------放下左left叉子");
right.release();
System.out.println("哲学家" + number + "--------放下右right叉子");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Semaphore> semaphores = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);
semaphores.add(semaphore);
}
Semaphore togetherSemaphore = new Semaphore(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new philosophy(i,semaphores)).start();
}
}
}
|
生产-消费者问题
问题阐述
- 2类进程共享1个公共的固定大小的缓冲区,缓冲区包含N个槽。
- 一类进程是生产者线程,负责将信息放入缓冲区;另一类是消费者线程,从缓冲区中取信息。
代码实现
实体类Ball
Ball.java
public class Ball {
private String number ;
private String color ;
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
|
ArrayBlockingQueue
public class ArrayBlockingQueueTest {
private BlockingQueue<Ball> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Ball>(1);
public int queueSize(){
return blockingQueue.size();
}
public void produce(Ball ball) throws InterruptedException{
blockingQueue.put(ball);
}
public Ball consume() throws InterruptedException {
return blockingQueue.take();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
final ArrayBlockingQueueTest box = new ArrayBlockingQueueTest();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (true){
Ball ball = new Ball();
ball.setNumber("乒乓球编号:"+i);
ball.setColor("yellow");
try {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+
":准备往箱子里放入乒乓球:--->"+ball.getNumber());
box.produce(ball);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+
":往箱子里放入乒乓球:--->"+ball.getNumber());
System.out.println("put操作后,当前箱子中共有乒乓球:--->"
+ box.queueSize() + "个");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i++;
}
}
});
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+
"准备到箱子中拿乒乓球:--->");
Ball ball = box.consume();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+
"拿到箱子中的乒乓球:--->"+ball.getNumber());
System.out.println("take操作后,当前箱子中共有乒乓球:--->"
+ box.queueSize() + "个");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
}
}
|
运行结果













